Controlling rhinoceros beetles in coconut trees is vital to preserve their health and productivity. Effective methods include traps, biological control with natural enemies, targeted application of insecticides, regular pruning, using physical barriers, maintaining good hygiene, early detection, and implementing quarantine measures. Adopting an Integrated Pest Management (IPM) approach is crucial for sustainable and eco-friendly control. Local agricultural authorities and experts can provide specific guidance on the best methods for a particular region.
Blog
-
Mites, thrips, and aphids are common pests that significantly impact roses. Mites cause leaf stippling and webbing, while thrips damage flower buds and transmit viruses. Aphids weaken roses by sap-sucking, producing honeydew that attracts sooty mold and transmitting viruses. Their rapid reproduction, weak plant defense, and attraction to roses exacerbate the problem. To combat these pests, integrated pest management practices are crucial, including early detection, pruning, beneficial insects introduction, and appropriate pesticide use when necessary. Seek advice from local horticultural experts for region-specific information and up-to-date control methods.
-
In Tamil Nadu during July 2023, the recommended varieties of marigolds are African, French, and Signet marigolds. African marigolds have a duration of 80-100 days and produce large, pom-pom-like blooms in yellow, orange, and gold. French marigolds have a duration of 60-80 days and come in a variety of colors and intricate petal patterns. Signet marigolds have a duration of 60-70 days, with small, single flowers in yellow or orange. These marigolds are compact and have finely divided foliage. By choosing these varieties, gardeners can enjoy a range of colors and fragrances in their Tamil Nadu gardens during July 2023.
-
Tomato plants in Tamil Nadu are vulnerable to diseases such as damping off, early blight, fusarium wilt, bacterial leaf spot, bacterial wilt, and tomato leaf curl virus. To prevent these diseases, it's important to use disease-resistant varieties, practice crop rotation, maintain sanitation, and implement proper cultural practices.
-
To control worms in a Brinjal farm in Tamil Nadu, it is essential to adopt integrated pest management techniques. These include implementing cultural practices such as crop rotation, maintaining proper sanitation, and removing infected plant debris. Encouraging natural predators like birds and beneficial insects can also help in controlling worm populations. Additionally, mechanical methods like handpicking and destroying worms or infested fruits can be effective for small-scale infestations. If necessary, the use of insecticides specifically labeled for Brinjal farms can provide chemical control. As for seasonal requirements, Brinjal farming in Tamil Nadu is commonly practiced during the summer (March to June) and rainy seasons (July to September). However, with appropriate management practices, it is possible to extend the cultivation period beyond these seasons.
-
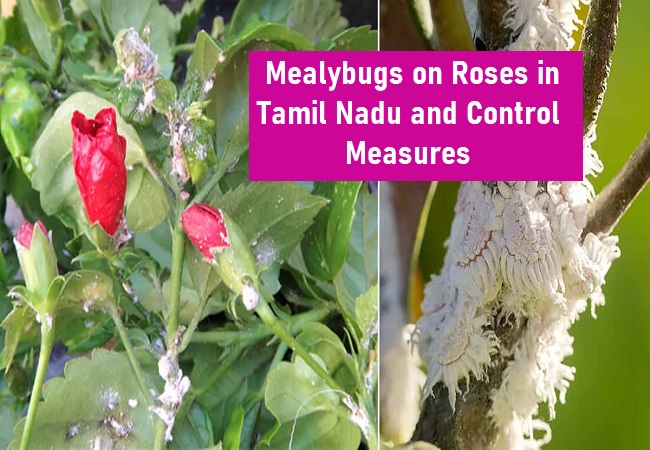
Employing an Integrated Pest Management (IPM) strategy that integrates various control methods is advisable for sustainable and effective management of mealybugs on roses in Tamil Nadu.
-
Recommended rose varieties for cultivation in Tamil Nadu include Hybrid Tea Roses (such as 'Papa Meilland'), Floribunda Roses (such as 'Iceberg'), Grandiflora Roses (such as 'Queen Elizabeth'), Climbing Roses (such as 'Don Juan'), and Miniature Roses (such as 'Chasin' Rainbows'). It is advisable to consult local horticultural experts for specific care instructions based on the growing conditions in Tamil Nadu.
-
In Tamil Nadu, the recommended time for applying NPK fertilizer to cotton crops is as follows: during the vegetative stage, apply NPK fertilizer 25-30 days after sowing with a ratio of 4:2:1 (N:P:K) to promote leafy growth. In the reproductive stage, apply NPK fertilizer 40-45 days after sowing with a ratio of 2:4:1 (N:P:K) to support flower and boll formation. For overall plant health and boll development, apply NPK fertilizer 60-65 days after sowing with a ratio of 2:1:2 (N:P:K). Additional NPK fertilizer may be applied during boll development if required. These recommendations serve as general guidelines, and consulting local agricultural experts or experienced farmers for site-specific advice is advisable.
-
Worms can adversely affect Brinjal cultivation in Tamil Nadu by damaging the roots, feeding on leaves, causing fruit damage, transmitting diseases, and weakening overall plant health. To mitigate these effects, farmers use strategies like chemical and biopesticides, crop rotation, resistant varieties, sanitation, and integrated pest management (IPM) approaches. Early detection and regular monitoring are essential for effective control.
-
Crops in Tamil Nadu vary based on the seasons and months. In January, crops like paddy, sugarcane, groundnut, tomato, onion, and brinjal can be cultivated. February is suitable for maize, ragi, pulses, cabbage, cauliflower, and carrot. March sees the cultivation of banana, chilli, green gram, coriander, and spinach. April is the time for rice, millets, sesame, beetroot, radish, and beans. May offers the opportunity to grow sugarcane, paddy, turmeric, pumpkin, and bitter gourd. In June, groundnut, pulses, tomato, onion, and cucumber are cultivated. July brings millets, paddy, brinjal, capsicum, and drumstick. August is the season for ragi, maize, chilli, coriander, and snake gourd. September sees the cultivation of pulses, tomato, onion, pumpkin, and ridge gourd. October is suitable for paddy, banana, turmeric, cauliflower, and carrot. In November, crops like sugarcane, groundnut, beans, radish, and spinach thrive. December brings rice, millets, sesame, beetroot, and bitter gourd to be cultivated. It's important to consider local conditions and consult experts for precise cultivation practices.